Our Specialities
Specialities in 
CHANDA DEVI TIWARI HOSPITAL
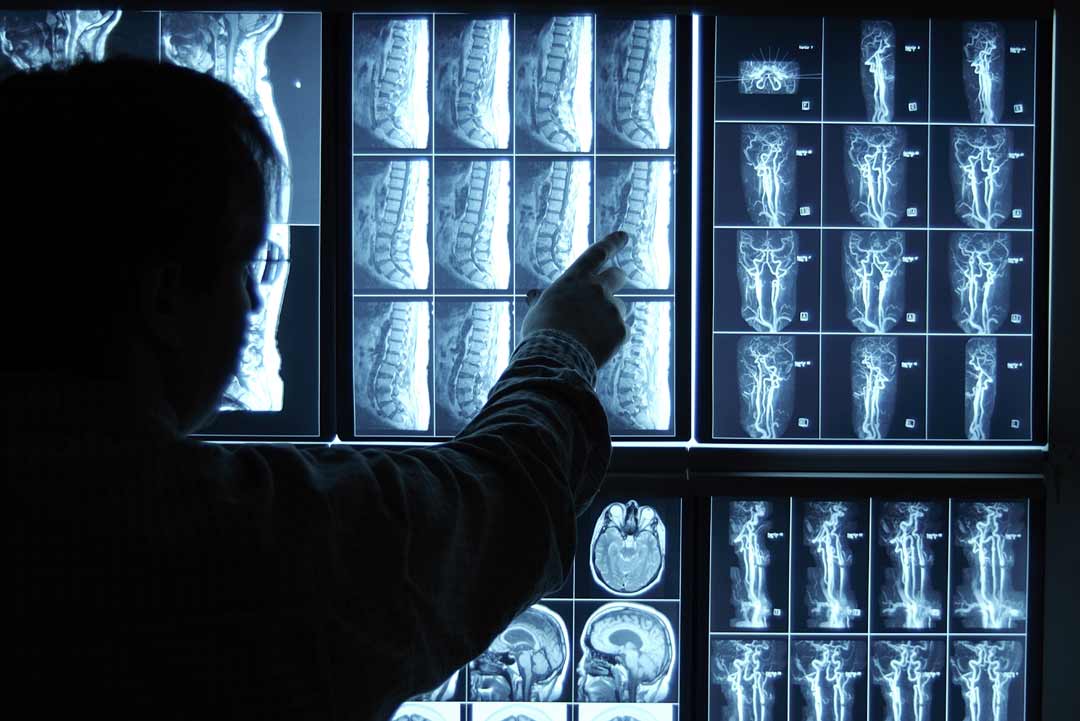
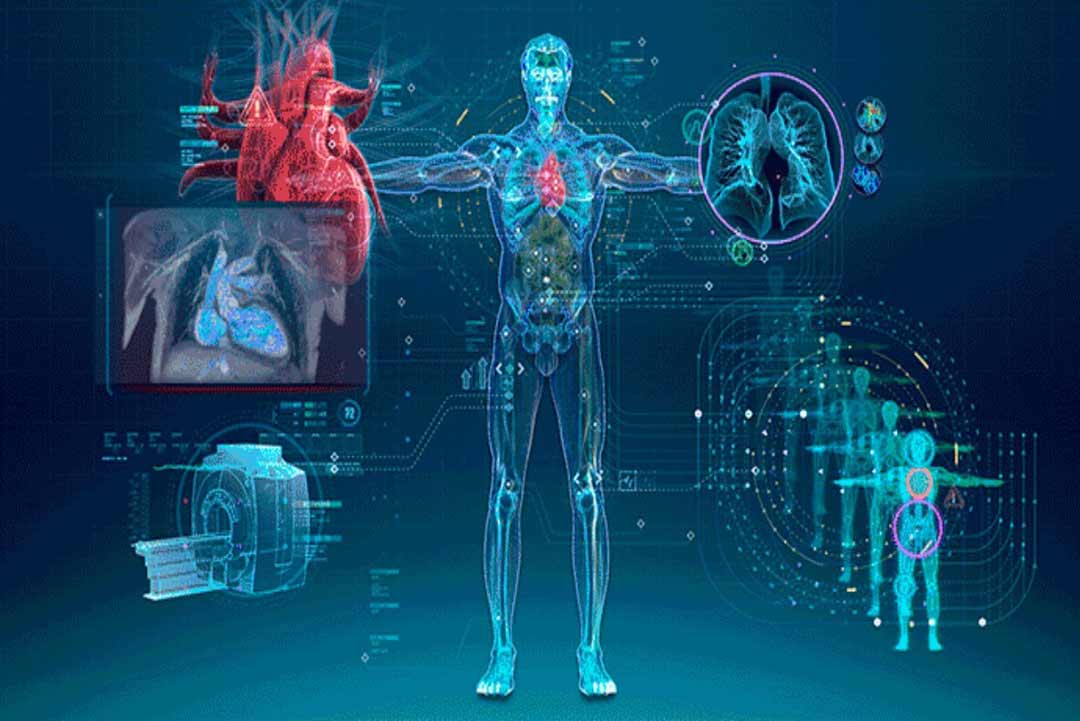
Radiology
Radiology
Radiology
We deals with radiant energy in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases. This field can be divided into two broad areas – diagnostic radiology and interventional radiology.
A Radiology is a specialization who deals with the study of images obtained by x-ray, ultrasound, CAT scans, or magnetic resonance imaging, and to the treatment of cancer by radiation therapy. Physicians who specialize in Radiology are called "Radiologist".
We use a variety of imaging techniques such as X-ray, ultrasound, computed tomography (CT), nuclear medicine including positron emission tomography (PET), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to diagnose and/or treat diseases.
X-RAY
X-rays are a type of radiation called electromagnetic waves. X-ray imaging creates pictures of the inside of your body. The images show the parts of your body in different shades of black and white. This is because different tissues absorb different amounts of radiation. Calcium in bones absorbs x-rays the most, so bones look white. Fat and other soft tissues absorb less, and look gray. Air absorbs the least, so lungs look black.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is acoustic (sound) energy in the form of waves having a frequency above the human hearing range. The highest frequency that the human ear can detect is approximately 20 thousand cycles per second (20,000 Hz). This is where the sonic range ends, and where the ultrasonic range begins. Ultrasound is used in electronic, navigational, industrial, and security applications. It is also used in medicine to view internal organs of the body.
Computed Tomography (CT)
Computed tomography (CT) is a diagnostic imaging test used to create detailed images of internal organs, bones, soft tissue and blood vessels. The cross-sectional images generated during a CT scan can be reformatted in multiple planes, and can even generate three-dimensional images which can be viewed on a computer monitor, printed on film or transferred to electronic media.
Our Services
Laparoscopy & Minimal Access Surgery
read more
Endoscopy Procedure
read more
General Surgery
read more
Obs & Gynaec
read more
Urology
read more
Denatal Surgery
read more
ENT
read more
Trauma & Orthopedic
read more
Cardiology
read more
General Medicine ICU
read more
Radiology and Imaging
read more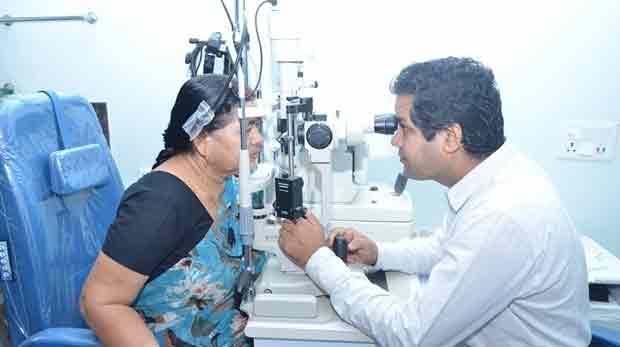
Opthal Surgery
read more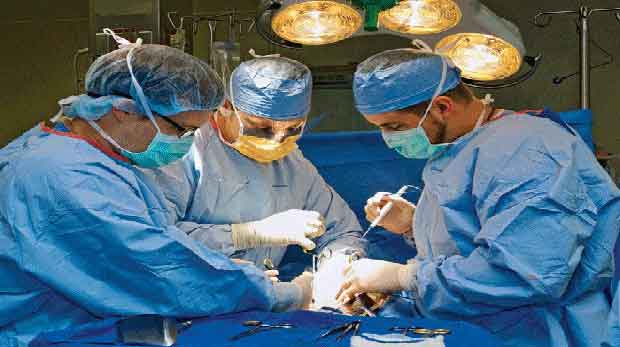
Intensive Care
read more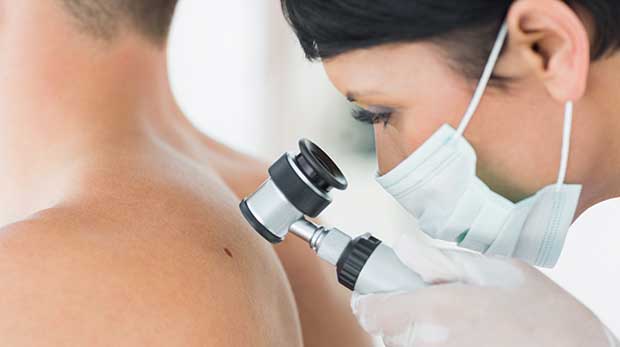
Skin Dermatology
read more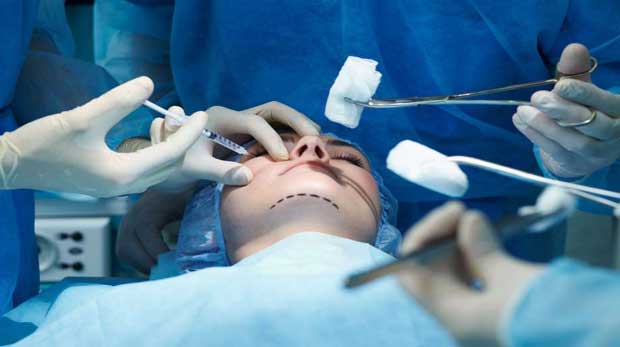
Plastic Surgery
read more
Paediatrics
read more