Our Facilities

24 X 7 Emergency Care Facility.
We provides emergent, urgent, and sub-urgent care to adult, pediatric, and obstratics patients. The 24 Hour Emergency Department is equipped to handle any medical emergencies around the clock every day. Our team of multi-disciplinary paramedics, nurses and doctors are at hand to ensure your condition is properly assessed and managed. Our specialists and surgeons are also on call 24 hours to help attend to your medical condition.
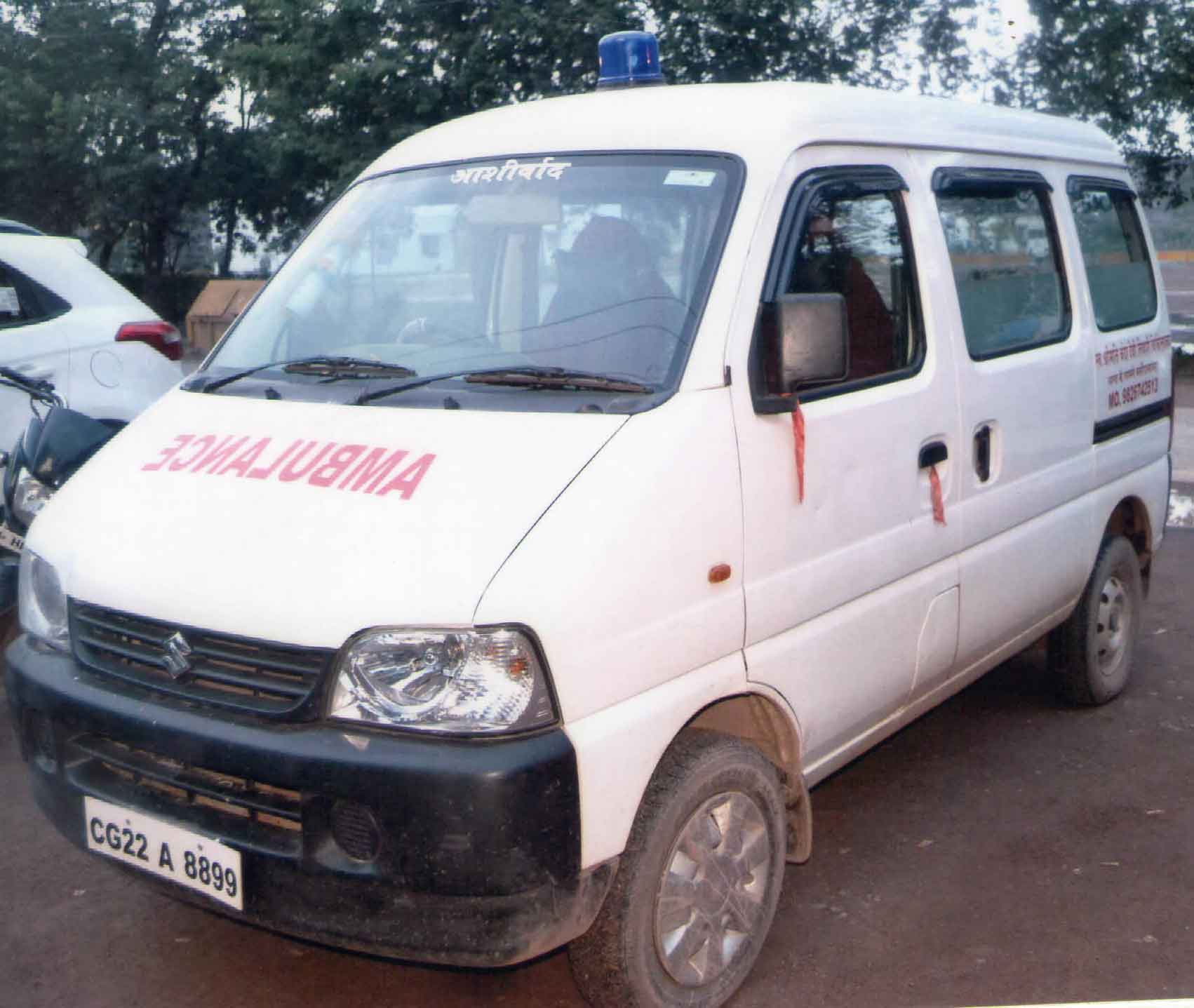

24 X 7 Ambulance Facility.
The nearest ambulance available in your locality will be rushed to your place, wherever you are, to bring your patient directly to Chanda Devi Tiwari hospital in the shortest possible time. And while the patient is on the way the Emergency Team at CDTH will keep the ICU Bed, O T, etc, ready so that no time is lost when the patient reaches hospital . No other hospital in Baloda bazar offers 24-hrs ambulance pick-up service. Not even during daytime .

Express Service For Emergency Patient.
Express service not only saves your time it also makes you free from the rush and allows you to directly consult with your respected physician to get better diagnosis and allows you to get a royality messages about the on calls Doctors visits at our centre for your better health .

24x7 Pharmacy Services/ Medical store
The mission of the pharmacy is to provide medications, other health care products, relevant information, professional services and to help people and society to make the best use of them. Every activity in the pharmacy is done with certain system and confidence, in order to give the right touch of professionalism and care.
We are best in delivering medicines, services and care of the patient.

Parking Facility Available
The mission of Parking Services is to provide courteous, safe, and efficient parking services for the campus community and public.Parking service is free for all 2 as well as 4 wheelers 24 x 7 .
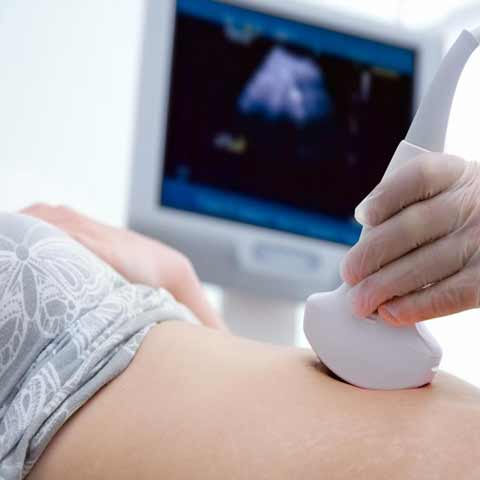
Sonography
Ultrasound imaging uses sound waves to produce pictures of the inside of the body. It is used to help diagnose the causes of pain, swelling and infection in the body’s internal organs and to examine a baby in pregnant women and the brain and hips in infants. It’s also used to help guide biopsies, diagnose heart conditions, and assess damage after a heart attack. Ultrasound is safe, noninvasive, and does not use ionizing radiation.
Ultrasound is safe and painless, and produces pictures of the inside of the body using sound waves. Ultrasound imaging, also called ultrasound scanning or sonography, involves the use of a small transducer (probe) and ultrasound gel placed directly on the skin. High-frequency sound waves are transmitted from the probe through the gel into the body. The transducer collects the sounds that bounce back and a computer then uses those sound waves to create an image. Ultrasound examinations do not use ionizing radiation (as used in x-rays), thus there is no radiation exposure to the patient. Because ultrasound images are captured in real-time, they can show the structure and movement of the body's internal organs, as well as blood flowing through blood vessels.
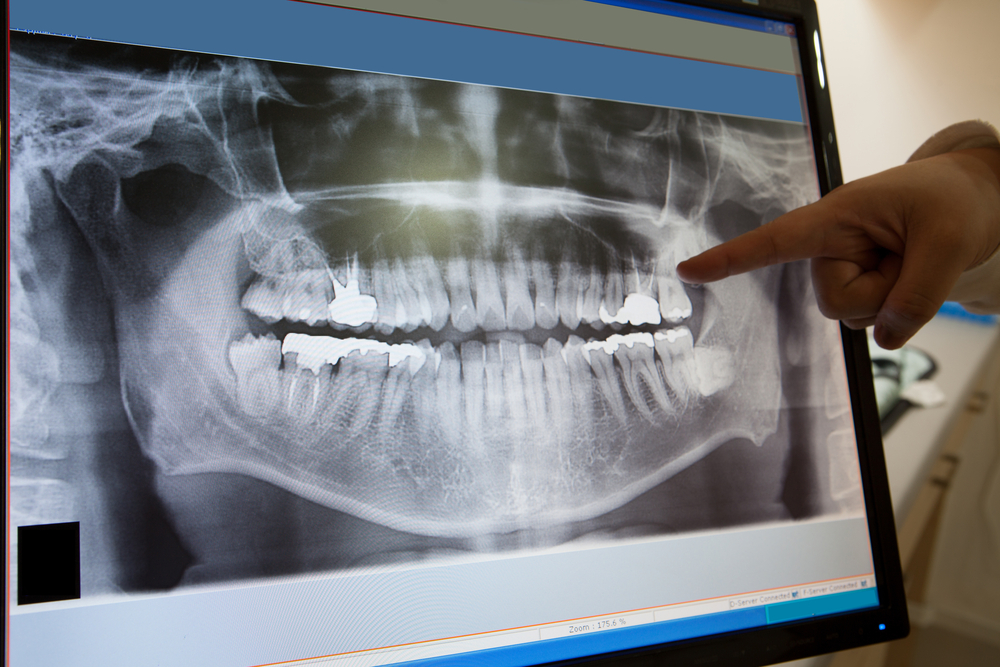
Digital X-Ray
X-rays are a form of electromagnetic radiation, as are radio waves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation and microwaves. One of the most common and beneficial uses of X-rays is for medical imaging. X-rays are also used in treating cancer and in exploring the cosmos.
Electromagnetic radiation is transmitted in waves or particles at different wavelengths and frequencies. This broad range of wavelengths is known as the electromagnetic spectrum. The EM spectrum is generally divided into seven regions in order of decreasing wavelength and increasing energy and frequency. The common designations are: radio waves, microwaves, infrared (IR), visible light, ultraviolet (UV), X-rays and gamma-rays.
Pathology Lab
Scientific Pathology offer a wide range of quality assured clinical and pathology investigation services using the latest technology, state of art equipments and testing facilities manned by experienced / trained doctors and technicians.