Our Specialities
Specialities in 
CHANDA DEVI TIWARI HOSPITAL
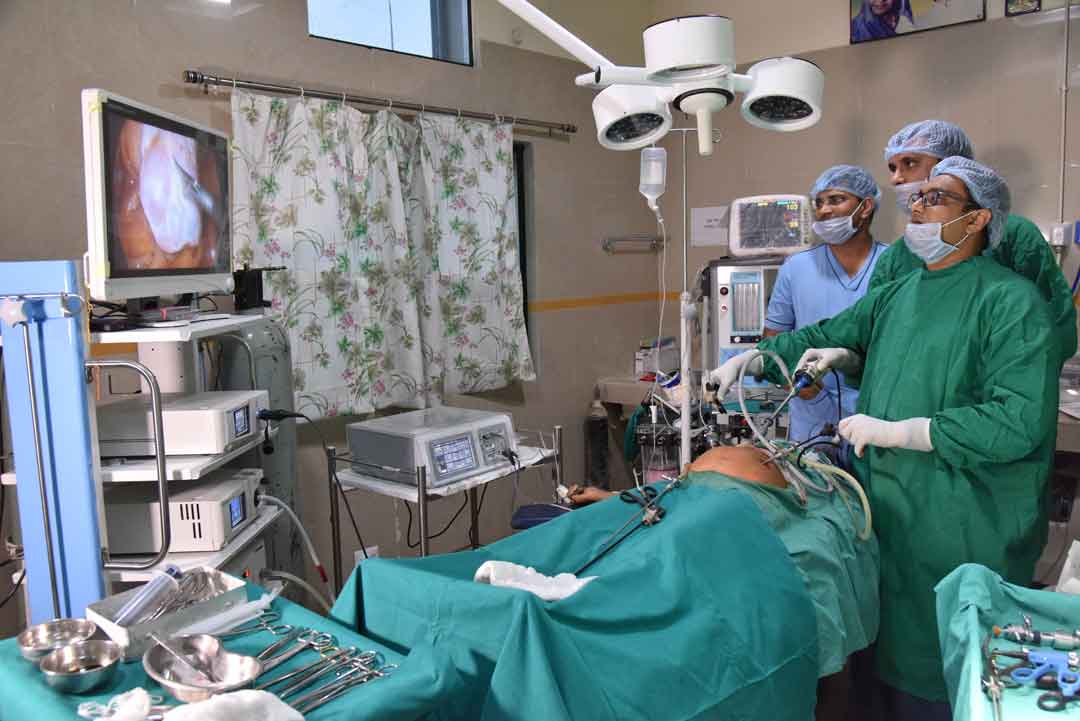
Laparoscopy & Minimal Access Surgery
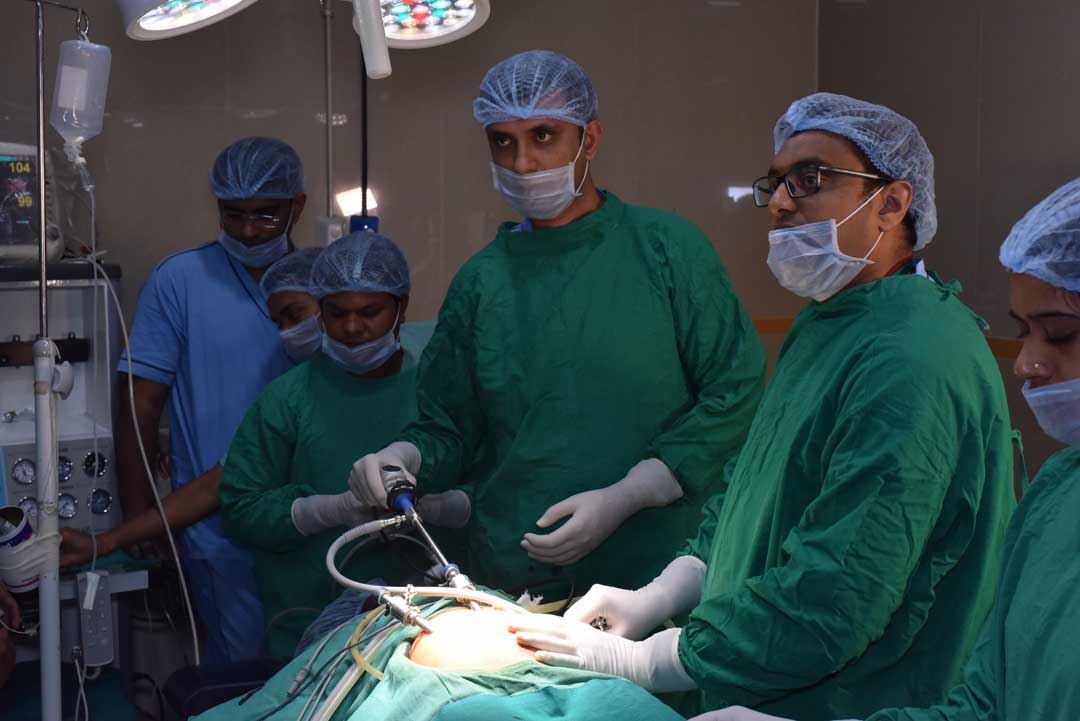
Laparoscopy & Minimal Access Surgery
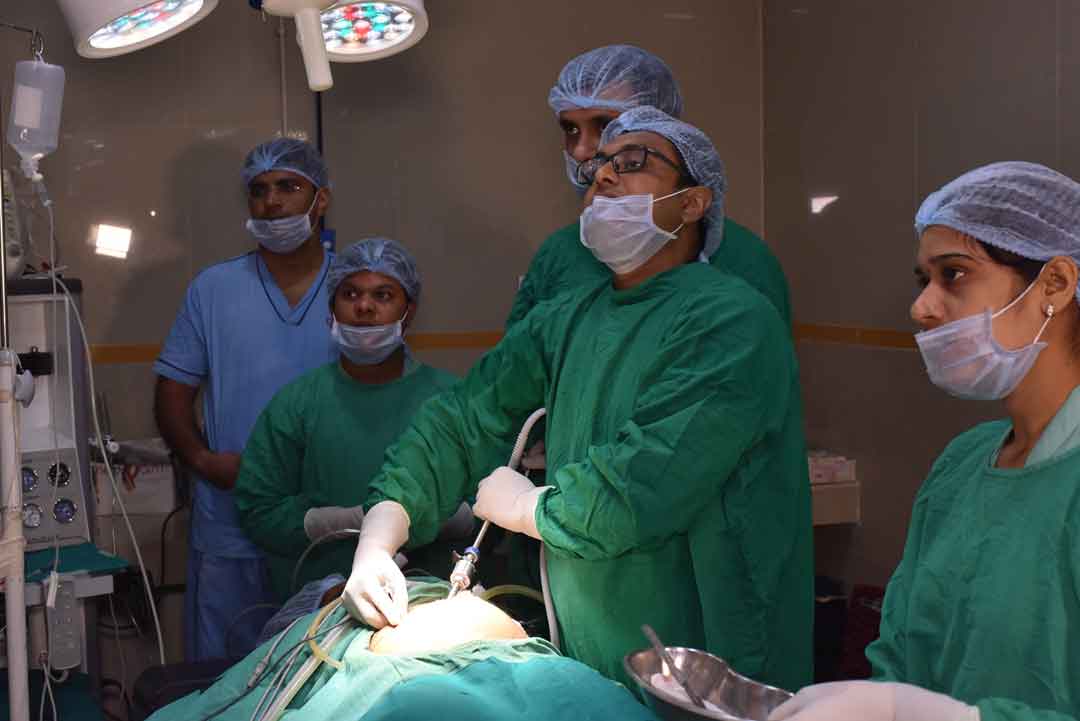
Laparoscopy & Minimal Access Surgery
For abdominal surgery Gyneacological Cancer & Pediatric procedures Open and Laparoscopic Approaches to Obesity Surgery The open approach involves an 8 to 10 inch incision to open the abdomen and perform the surgery in open view of the surgical team.
The laparoscopic approach creates five or six small incisions (1/4 or 1/2 inch long) instead of the one larger incision. In the laparoscopic method, a small fiberoptic tube (the laparoscope), connected to a video camera, is inserted through the small abdominal incisions. This gives the surgeon a magnified view of the patient's internal organs on a television screen next to the operating table.
Using advanced technology; surgeons can now perform laparoscopic surgery. This technique allows surgeons to make small pencil-sized holes in the body while video equipment is used to provide a magnified view of the surgical site. Instruments are used to perform the surgery through the incisions so patients experience smaller scars, fewer complications, shorter hospital stays, and faster recoveries.
Types of Surgical Procedures Performed
Abdominal Surgery
Abdominal surgery refers to any surgical operation on abdominal organs, including the stomach, gallbladder, small intestine, large intestine, appendix, liver, pancreas, spleen, esophagus and appendix. The procedures may be performed for a variety of reasons, including infection, obstruction, tumors or inflammatory bowel disease.
Minimal Access Gyneacology
The minimal access surgery service at the Royal Free London encompasses: Diagnostic hysteroscopy to investigate abnormal uterine bleeding. This is either done as day surgery or in a 'one stop' out-patient clinic; operative hysteroscopy for hysteroscopic myomectomy, endometrial ablation, metroplasty and adhesiolysis; and complex operative laparoscopy for ovarian cysts, endometriosis, adhesions, infertility, pelvic pain and fibroids. For fibroids unsuitable for endoscopic surgery we offer open myomectomies. We also offer uterine artery embolisation in conjunction with consultant radiologists.
The benefits of minimally invasive robotic surgery can include:
Hysterectomy
Hysterectomy is a surgery to remove the uterus. It prevents future pregnancy and eliminates fibroid-related bleeding and pressure symptoms.
Myomectomy
Myomectomy is the surgical removal of uterine fibroids without the removal of the uterus. There are several techniques that may be used, and the choice of the technique depends on the location and size of the fibroids as well as the characteristics of the woman. It is sometimes impossible to remove all the fibroids, and new fibroids may grow after a myomectomy. Though myomectomy is the only accepted procedure for fibroids in a woman who wants to maintain fertility, a myomectomy may lead to scarring that can negatively affect future fertility. Following a myomectomy, cesarean delivery is frequently recommended to prevent the myomectomy scar from breaking open during labor. Types of myomectomies include:
Ovarian Surgery
Surgery is the main treatment for most ovarian cancers. How much surgery you have depends on how far your cancer has spread and on your general health. For women of childbearing age who have certain kinds of tumors and whose cancer is in the earliest stage, it may be possible to treat the disease without removing both ovaries and the uterus.
Laparoscopic Harnia
Our Services
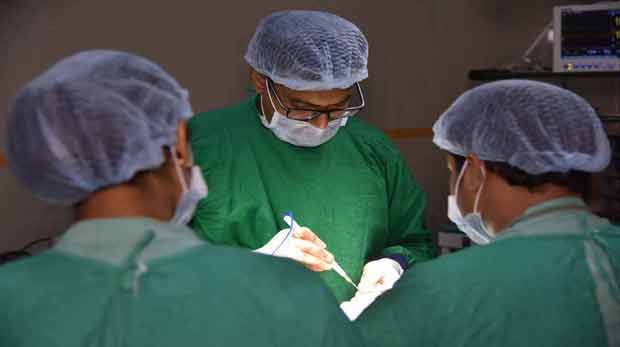
Laparoscopy & Minimal Access Surgery
read more
Endoscopy Procedure
read more
General Surgery
read more
Obs & Gynaec
read more
Urology
read more
Denatal Surgery
read more
ENT
read more
Trauma & Orthopedic
read more
Cardiology
read more
General Medicine ICU
read more
Radiology and Imaging
read more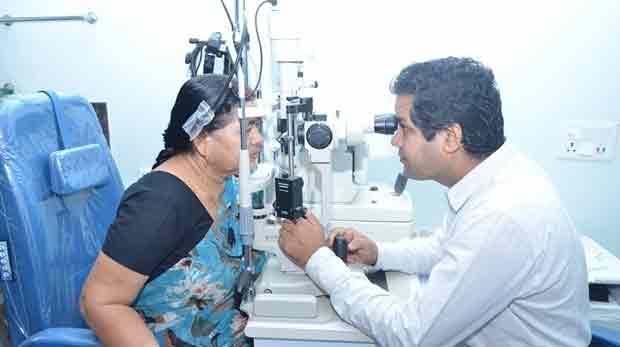
Opthal Surgery
read more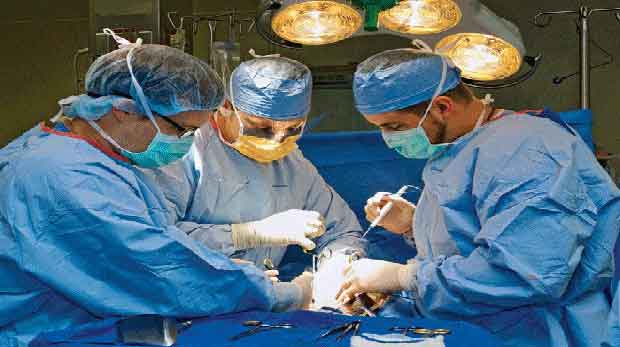
Intensive Care
read more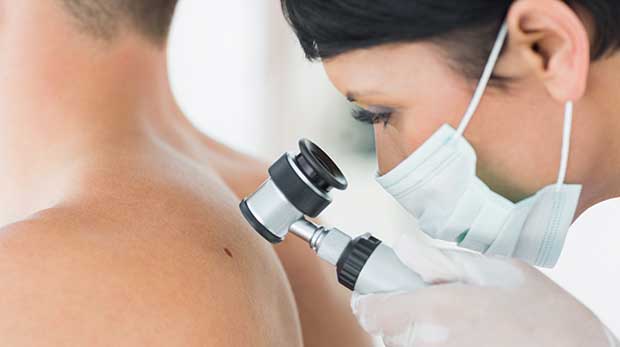
Skin Dermatology
read more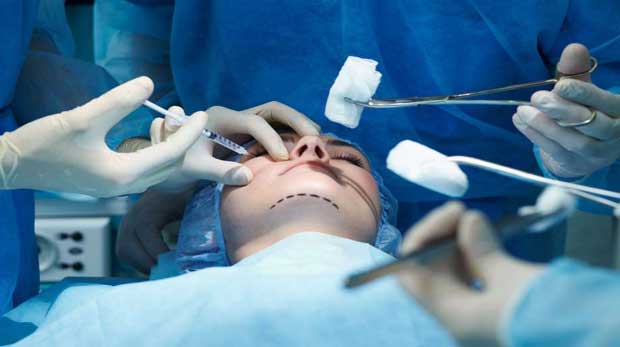
Plastic Surgery
read more
Paediatrics
read more